
This video shows detailed about top drive from Varco with a lot of operation aspect and it will help you learn a lot of details about Top Drive. We already add full the video transcript in order to help people understand all details.

Reservoir drive mechanism is the manner in which various energy sources in a reservoir provide energy to flow fluids in reservoir to surface. Recovery of reservoir fluid is categorized into three categories (primary, secondary, and tertiary recover).
This is the first mechanism which is carried out by natural energy in a reservoir.
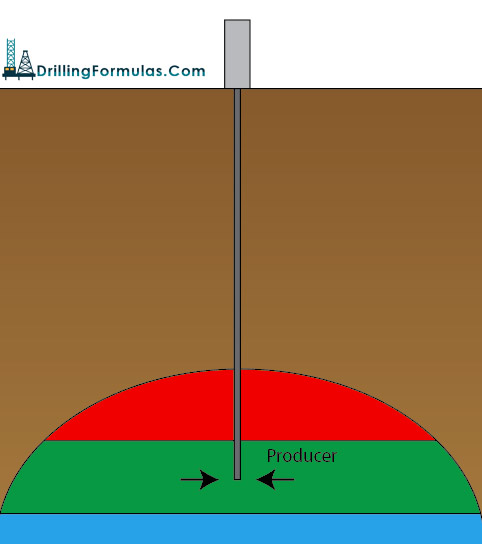
Figure 1 – Primary Recovery Continue reading

When there is only one type of fluid flowing through porous media, the permeability for this case is called “absolute permeability.” However, when there is more than one type of fluids present in a rock, a permeability of each fluid to flow is decreased because another fluid will be moving in the rock as well. A new term of permeability called “effective permeability” is a permeability of a rock to a particular fluid when more than one type of fluid is in a rock.
Reservoir consists of three fluids (gas, oil, and water) so these are commonly used abbreviations for effective permeability for each fluid.
kg = effective permeability to gas
ko = effective permeability to oil
kw = effective permeability to water
Normally, it is common to state effective permeability as a function of a rock’s absolute permeability. Relative permeability is defined as a ration of effective permeability to an absolute permeability of rock. The relative permeability is widely used in reservoir engineering. These functions below are the relative permeability of gas, oil, and water.
Relative permeability to gas – krg = kg÷k
Relative permeability to oil – kro = ko÷k
Relative permeability to water – krw = kw÷k
Where;
k = absolute permeability

Capillary pressure is a force due to differentials between fluid densities in a rock that can force pull hydrocarbon through the pores of a rock so a transition zone between fluids occurs.
Let’s make it simple. If we put a small tube in water overlaid by oil, water will rise up into the tube due to capillary pressure (Pc). For this situation, the capillary pressure (Pc) is the difference in pressure across the curved interface between the fluids (oil and water) shown in Figure 1.
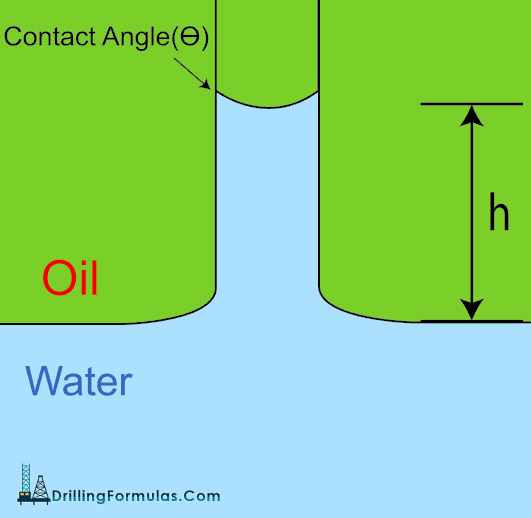
Figure 1 – Capillary Diagram Continue reading

Wettability is a tendency of fluid to stick to the surface of formation when other types of fluid are present. Wettability of rock is measured by a core analysis in a laboratory and typically a laboratory measure contact angle between the fluid and the rock.
Wettability of rock is classified by the angle of contact, which is divided into 3 categories.
Water wet – contact angle (θ) is less than 90 degrees

Figure 1 – Water Wet Continue reading