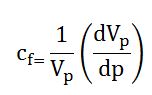Fluid saturation is how much each fluid is present in pore spaces of a rock. This will affect the ability of each fluid flow through porous media. This is one of critical values for reservoir engineering since many engineering calculations need fluid saturation values.
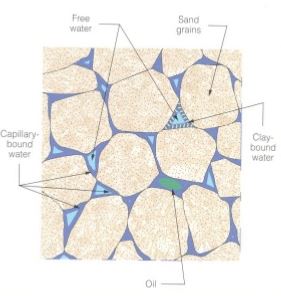
Fluid Saturation in Rock
Fluid saturation is expressed in terms of volume of fluid divided by total pore space.
Gas saturation (Sg) = Vg ÷ Vp
Oil saturation (So) = Vo ÷ Vp
Water saturation (Sw) = Vw ÷ Vp Continue reading